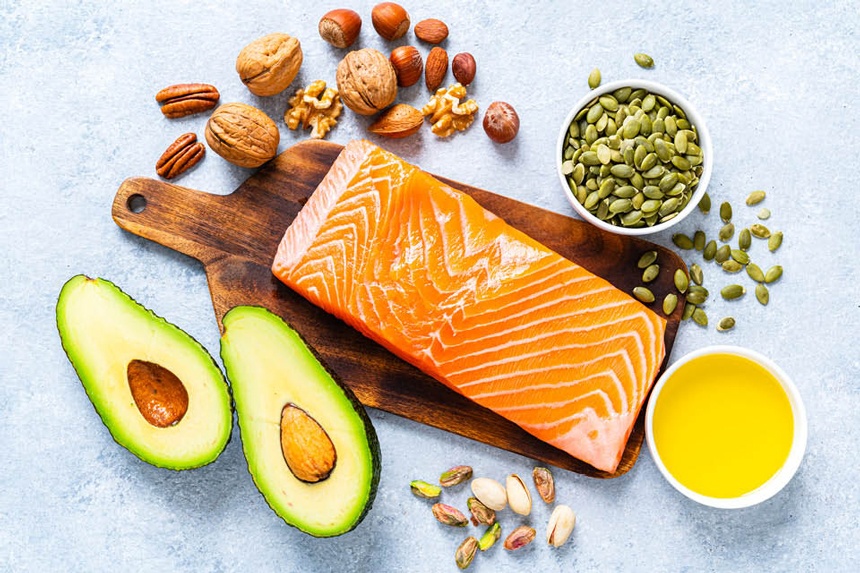
Leading health entities advocate for adults to intake 250–500 milligrams (mg) daily of essential fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), achievable through bi-weekly servings of fatty fish. For a plant-derived omega-3, alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), the recommended Adequate Intake stands at 1,600 mg for men and 1,100 mg for women, as per the National Institutes of Health.
Omega-3 fats, vital for heart, brain, and overall health, are abundant in fatty fish, algae, and certain plant foods. Below, we explore twelve foods exceptionally rich in omega-3, incorporating additional insights into each food’s unique benefits.
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Herring
- Oysters
- Cod Liver Oil
- Anchovies
- Caviars
- Sardine
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseed
- Soybeans
- Walnuts [1]
Salmon
Salmon stands out in the culinary world for its exceptional nutrient profile, including high-quality protein, vitamins D and B, and selenium. A 100-gram serving provides 2,150 mg of EPA and DHA, contributing to a lower risk of heart disease, dementia, and depression. This rich content underscores salmon’s role in a balanced diet, supporting overall health and well-being.
The consumption of salmon, particularly wild-caught, offers additional benefits such as a lower fat content compared to farmed varieties. Its versatility in recipes from around the globe makes salmon a favorite among health-conscious individuals. [2] [3]