Cancer is a multifaceted illness with various potential causes. While the definitive answers to its cause remain elusive, it is evident that numerous factors contribute to its development. Genetic predisposition and family history play a role, but lifestyle choices wield a more significant influence, contributing to 80 to 90 percent of malignant tumors.
Among these lifestyle factors, diet has the most importance. Several studies underscore the association between certain foods and an increased risk of specific cancers. Some foods elevate the risk of conditions like type 2 diabetes and obesity, which, in turn, increases the likelihood of developing cancer. Additionally, certain foods contain carcinogens, posing a direct risk of cancer.
However, exposure to carcinogens does not guarantee cancer development, as genetics and the level/duration of exposure also factor in. Top among these causes are:
- Fried foods
- Processed meats
- Dairy
- Alcohol
- Overcooked foods
- Sugar and refined carbs
- Microwave Popcorns
- Farm Fish
- Pickled Food
- Hydrogenated Oil [1]
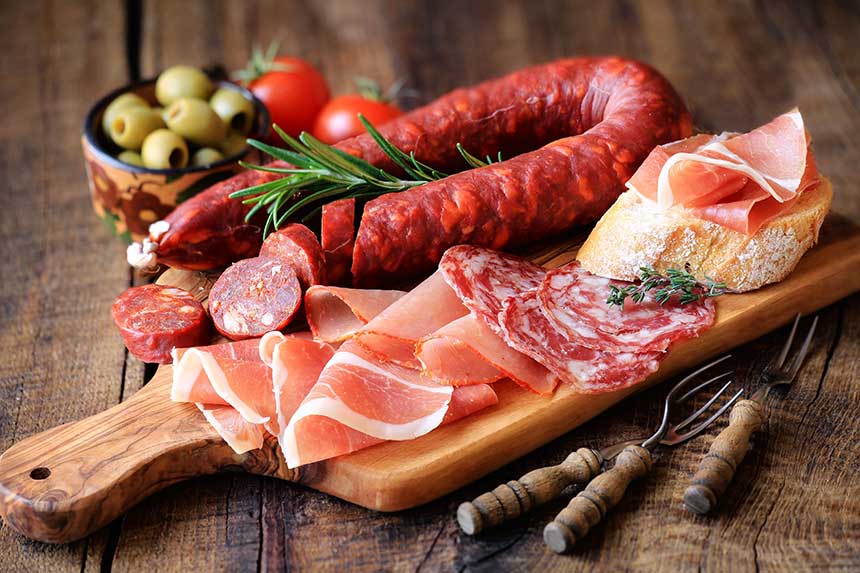
Processed Meats
Processed meats like hot dogs, salami, and bacon undergo preservation methods involving smoking, salting, or curing. Unfortunately, these processes can generate carcinogenic substances. For instance, curing meats with nitrites can form N-nitroso compounds, while smoking meats can produce carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Studies highlight the association between processed meat consumption and an increased risk of colorectal, stomach, and breast cancers. The intake of processed meat significantly correlates with a higher likelihood of developing these types of cancers, making it crucial to limit your consumption for better health outcomes. [2] [3] [4]