High Blood Calcium Levels
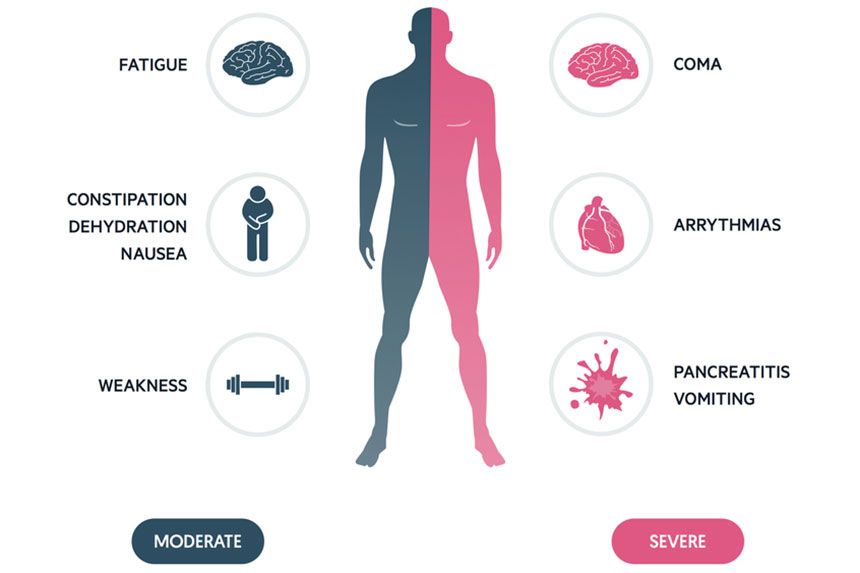
Vitamin D’s role in calcium absorption can, when in excess, elevate blood calcium to harmful levels. Hypercalcemia, marked by elevated calcium, manifests through digestive issues, mental disturbances, dehydration, and more severe kidney and heart conditions.
Chronic overdose situations reveal the risks of ignoring dosage recommendations, with symptoms often necessitating immediate medical intervention. Understanding the relationship between vitamin D and calcium underscores the importance of balanced supplementation. [4]
Gastrointestinal Distress
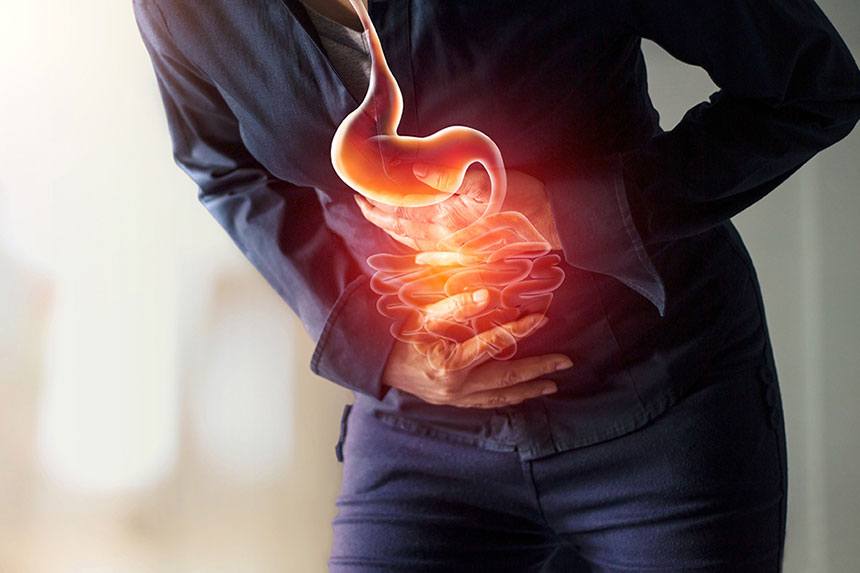
Excessive vitamin D can lead to gastrointestinal symptoms due to heightened calcium levels. Nausea, vomiting, and constipation are common, with severity correlating to the extent of overdose. Individual responses vary, but extreme cases, such as significant overdosing, have led to acute symptoms requiring medical attention.
These instances, including unintentional overconsumption due to mislabeled supplements, underscore the necessity of cautious supplement selection and adherence to recommended dosages.





